

Understand Acute Pancreatitis Risk
Continuing to do what you can to lower very high triglycerides may help reduce your risk of acute pancreatitis.
Very high triglycerides (TGs) may lead to acute pancreatitis
Triglyceride levels over 880 mg/dL while fasting may be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
Very high triglyceride levels could be a sign of Familial Chylomicronemia Syndrome (FCS). A person may be diagnosed with FCS as a baby or young child, but some people may not have symptoms until they are adults. People with FCS see an average of 5 doctors before they are finally diagnosed.
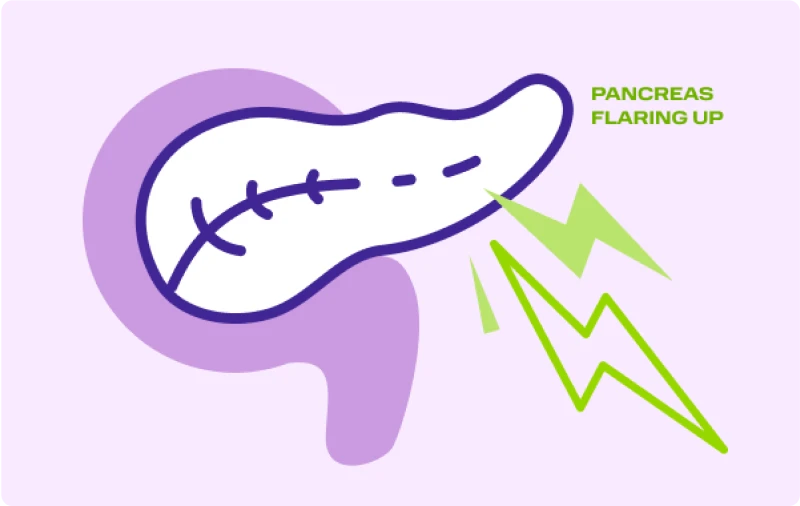
Whether caused by FCS or not, living with untreated very high triglyceride levels increases the risk of acute pancreatitis—a serious, potentially life-threatening condition often requiring hospitalization.
An increasing risk of acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis from high triglycerides is often more severe and deadlier than other causes of acute pancreatitis. Even one event can greatly increase the chance of another in the future. Repeated flares can damage the pancreas, leading to chronic pancreatitis and other serious life-threatening complications.
Sources: 1. Grundy SM et al. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(24):e285-e350. 2. Handelsman Y et al. Endocr Pract. 2020;26(10):1196-1224. 3. Mszar R et al. J Clin Med. 2023;12(4):1382. 4. Sanchez RJ et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Jul 18;20(1):72.
What is FCS?

Scroll to Explore
People with FCS have triglyceride levels 10 to 100 times higher than normal. When your body has too many triglycerides in your blood, it can cause problems such as:
- Acute pancreatitis
- Enlarged liver and/or spleen
- High blood pressure
- Physical weakness
- Fatigue
- Nerve pain or numbness in your hands and feet
- Diabetes
- Bloating
- Indigestion
- Eating disorders
- Problems thinking
- Eye problems
- Fatty lumps on your body
How old were you when you were diagnosed with FCS or very high triglycerides?
Please select your response. Your answer is confidential.
Thank you for your response.
This information will help shed light on the challenges faced by people living with very high triglycerides.
Hear from others living with FCS
Back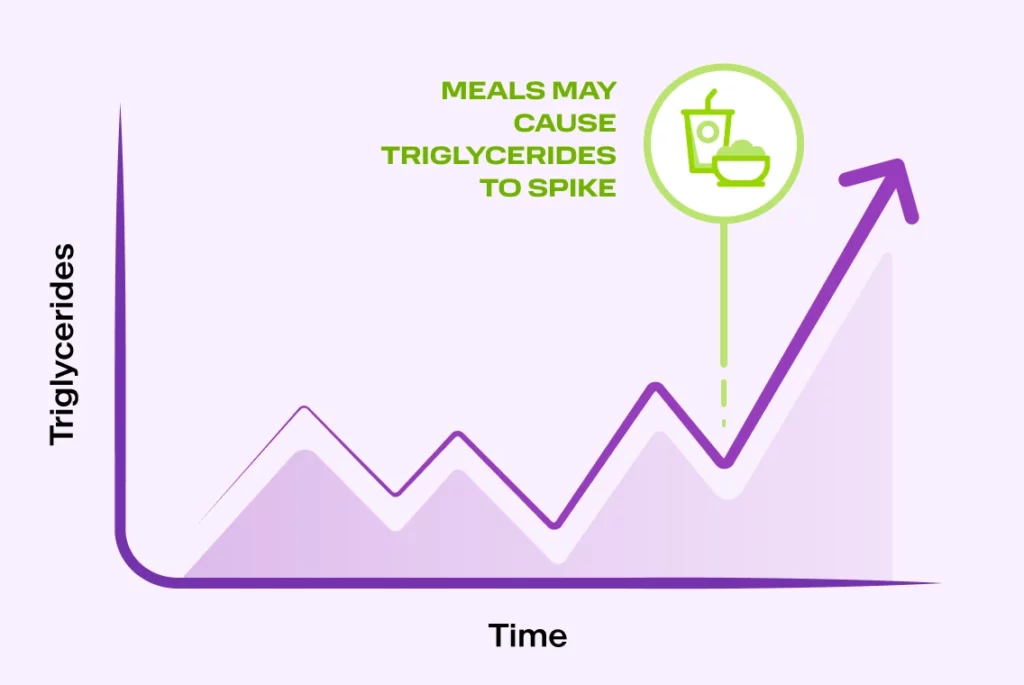
With FCS, meals may cause spikes in triglyceride levels
Triglycerides are a kind of fat that comes from the food you eat and are stored in chylomicrons. Just one meal may cause a spike in triglycerides that could sneak up on a person living with FCS and may cause acute pancreatitis.
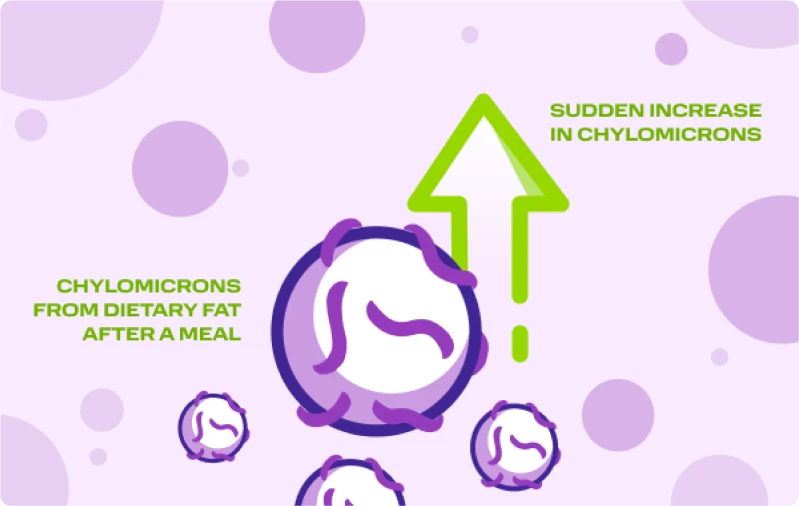
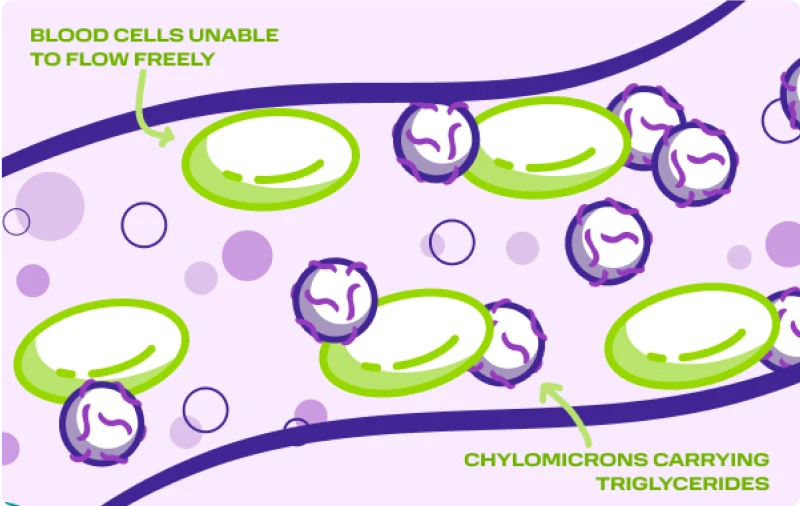
Chylomicrons and the risk of pancreatitis
Your body creates particles called chylomicrons from fat in your diet. Chylomicrons move triglycerides to where your body needs them.
Scroll to Explore

Regular testing keeps you informed of triglyceride levels
If you are diagnosed with FCS, talk to your doctor about scheduling regular monitoring with a team of specialists, such as lipidologists, endocrinologists, cardiologists, pancreatologists, primary care physicians, dietitians, and your caregiver. Lab tests every 3 months help track fasting triglyceride levels.
AACE, American Association of Clinical Endocrinology.
Learn what’s going on in the world of lipids
We’ll get there [soon]
Traditional options may not work
For some people, traditional therapies and strict diets aren’t enough to lower triglyceride levels or risk of pancreatitis.
Additional Support
Nutrition, exercise, and hydration are important to managing high triglycerides in your everyday life.